How Does Creatine Work | Combat Creatine Supplements
How Does Creatine Work? A Deep Dive into This Powerful Supplement
Creatine is one of the most popular supplements for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone looking to boost muscle growth and performance.
But how does creatine actually work?
In this article, we’ll explore the science behind creatine, its effects on the body, and why it’s a go-to supplement for increasing muscle strength and size.
Whether you’re new to creatine or looking to understand its potential benefits better, this guide will give you all the answers.
Outline of Topics
- What Is Creatine?
- How Does Creatine Work in the Body?
- What Are the Benefits of Creatine?
- Why Do People Take Creatine Supplements?
- How Creatine Affects Muscle Growth
- What Is Creatine Monohydrate?
- Is Creatine Safe for Most People?
- Should Women Use Creatine?
- What Are the Side Effects of Creatine?
- How Much Creatine Should You Take?
1. What Is Creatine?
Creatine is a natural compound found in the body and in certain foods like meat and fish. It is made from amino acids and stored primarily in skeletal muscle.
The body’s creatine levels are crucial for energy production during high-intensity activities.
To dive deeper into this compound, check out our Ultimate Guide to Creatine Supplements.
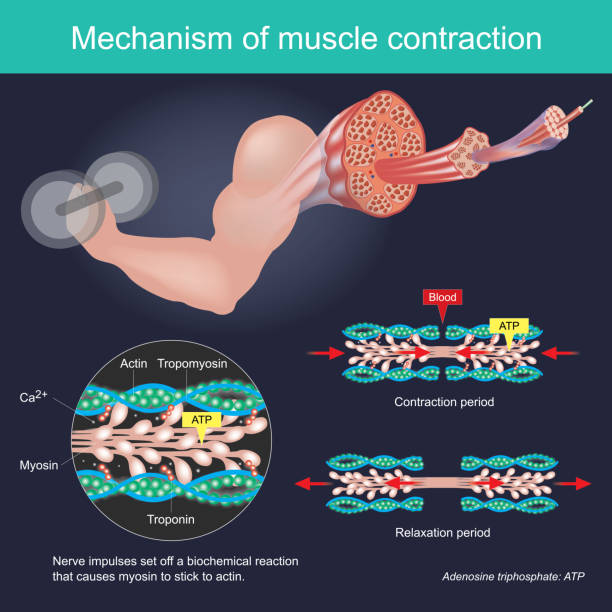
2. How Does Creatine Work in the Body?
Creatine works by increasing the levels of phosphocreatine, also known as creatine phosphate, in muscle cells.
This compound helps regenerate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the body’s main energy source for quick and intense movements like lifting weights or sprinting.
To learn more about this process, read How Does Creatine Work?.

3. What Are the Benefits of Creatine?
- Increased Muscle Strength and Mass: Creatine supplementation can help increase muscle strength by enhancing energy availability.
- Improved Muscle Recovery: Studies suggest that creatine may reduce muscle recovery time after intense exercise.
- Enhanced Performance: Creatine is effective for short bursts of high-intensity exercise, such as weightlifting and sprinting.
For a detailed breakdown of its benefits, visit Creatine Supplementation Benefits for Muscle Damage, Recovery, and Performance.
4. Why Do People Take Creatine Supplements?
Many athletes take creatine supplements to improve performance, build muscle mass, and support muscle recovery.
Since creatine is a natural compound, supplementing with creatine provides a way to boost levels beyond what the body produces or gets from diet alone.
Explore the differences between Creatine Powder vs. Pills to find the right option for your needs.
5. How Creatine Affects Muscle Growth
Creatine helps increase muscle mass by enhancing water content in muscle cells and improving the body’s capacity to perform total work during resistance training.
This effect of creatine supplementation directly supports muscle growth over time.
Read more about this process in Choosing the Right Type of Creatine.
6. What Is Creatine Monohydrate?
Creatine monohydrate is the most common and well-studied form of creatine. It is highly effective for increasing muscle creatine levels and has been shown to be safe for most people when taken at recommended doses.
For more insights, check out our guide on Creatine Monohydrate Gummies.
7. Is Creatine Safe for Most People?
Yes, creatine is safe for most people. Research on creatine, including its safety and efficacy, has consistently shown that it is one of the most studied and reliable supplements available.
However, people with kidney issues should consult a healthcare provider before using creatine.
Learn more about Creatine Supplementation Side Effects.
8. Should Women Use Creatine?
Yes, women can benefit from creatine supplementation. Creatine for women supports muscle recovery, improves energy levels, and enhances strength.
Studies have found that creatine supplementation may also help preserve muscle mass, especially during weight loss.
Discover the Top 10 Reasons Women Should Take Creatine.

9. What Are the Side Effects of Creatine?
While creatine is generally safe, some people may experience mild side effects such as:
- Water retention (muscles hold more water).
- Stomach discomfort when taking high doses.
- Rarely, muscle cramping.
It is advisable to take creatine supplements in the recommended dose to minimize side effects.
For more details, visit Creatine Supplement Pros and Cons.
10. How Much Creatine Should You Take?
A common dose of creatine is 5 grams per day. This amount is sufficient for maintaining elevated muscle creatine levels.
During a loading phase, people often take 20 grams per day, split into 4 doses, for 5–7 days to saturate muscle stores more quickly.
For an in-depth guide, read Creatine Loading Phase Explained.

Summary: Key Points About Creatine
- What It Is: Creatine is a natural compound that boosts energy in muscle cells.
- How It Works: It increases ATP production, improving performance and recovery.
- Benefits: Includes enhanced muscle growth, strength, and recovery.
- Safety: Safe for most people when taken in recommended doses.
- Dosage: Typically, 5 grams per day is effective.
By understanding how creatine works, you can decide if this supplement is right for your fitness goals.
For More Training Advice + Diet and Lifestyle visit us Combat Creatine
PS: Make sure you check out the rest of our Creatine Guides:
Creatine
Enhancing BJJ Performance: The Benefits of Creatine for Jiu Jitsu Athletes
Does Creatine Make Your Penis Bigger?
Does Creatine Cause Hair Loss?
When to Take Creatine: Pre vs Post Workout
Is Creatine Safe for Teen Athletes
Can You Take Creatine for Weight Loss
Should I Take Creatine on Rest Days or Off Days
Can You Take Creatine Before Bed
Can You Take Creatine Without Working Out?
Can You Mix Collagen and Creatine in One Drink?
What Happens When You Stop Taking Creatine
The Impact of Alcohol and Creatine
Can You Bring Creatine Powder on a Plane












