L-Carnitine vs. Acetyl-Carnitine: Key Differences and Benefits
L-Carnitine and Acetyl-L-Carnitine: How These Amino Acids Fuel Energy, Fight Fat, and Boost Brain Function
If you’ve been searching for ways to supercharge your energy, enhance cognitive function, and tap into fat-burning potential, look no further than l-carnitine and acetyl-l-carnitine.
These amino acid derivatives are often overlooked yet play a crucial role in energy metabolism, brain health, and fat utilization.
Whether you’re a fitness enthusiast, someone managing type 2 diabetes, or simply looking to improve your well-being, understanding the effects of l-carnitine could be a game-changer.
In this article, we break down the benefits of l-carnitine, compare l-carnitine and acetyl-l-carnitine, and show you how they impact carnitine levels, oxidative stress, and more.
Backed by research and clinical insight, this post will help you make informed decisions about carnitine supplementation.
Article Outline
- What is L-Carnitine and Why Is It Important?
- What Does L-Carnitine Do in the Body?
- L-Carnitine vs. Acetyl-L-Carnitine: What’s the Difference?
- How Does Acetyl-L-Carnitine Support Brain Function?
- Can L-Carnitine Help with Fat Loss and Energy Production?
- Does L-Carnitine Help Manage Type 2 Diabetes?
- What Are the Main Benefits of L-Carnitine Supplementation?
- How Much L-Carnitine Do You Need Daily?
- Who Might Be Deficient in Carnitine?
- Should You Take Both L-Carnitine and Acetyl-L-Carnitine?
1. What is L-Carnitine and Why Is It Important?
L-carnitine is a naturally occurring compound derived from the amino acid l-carnitine. It’s considered a conditionally essential nutrient, meaning the body typically produces enough unless under stress or due to certain health conditions. L-carnitine plays a crucial role in transporting fatty acids into the mitochondria to be burned for energy.
Your body synthesizes l-carnitine mainly in the liver and kidney, but it's stored in tissues that use fatty acids as a fuel source, like skeletal and cardiac muscle. According to the National Institutes of Health and the Office of Dietary Supplements, dietary l-carnitine also comes from red meat and dairy products.
For people on vegetarian or vegan diets, l-carnitine supplementation might be necessary to maintain carnitine levels for optimal health and performance.
2. What Does L-Carnitine Do in the Body?
The role of l-carnitine in the body centers around energy production. It works by transporting fatty acids into the mitochondria, the cell’s powerhouse, where they are burned for energy. This makes it vital for athletes and anyone seeking improved energy metabolism and physical performance.
Another key function is its ability to reduce oxidative stress, which is linked to aging and several chronic conditions. The effect of l-carnitine supplementation on oxidative stress is particularly beneficial in reducing oxidative damage at the cellular level.
Studies also show l-carnitine may influence insulin sensitivity, cardiovascular health, and recovery from exercise by supporting the mitochondrion in producing energy efficiently.
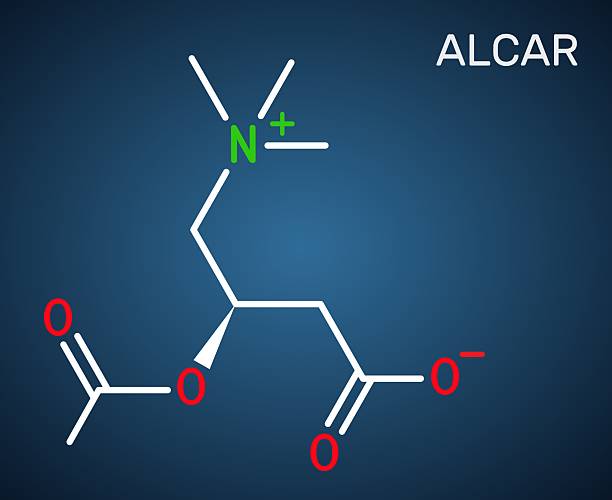
3. L-Carnitine vs. Acetyl-L-Carnitine: What’s the Difference?
Both l-carnitine and acetyl-l-carnitine (often referred to as ALCAR) are forms of carnitine, but they serve slightly different functions.
Acetyl-l-carnitine includes an acetyl group that enables it to cross the blood-brain barrier, making it especially effective for brain function and cognitive benefits. It's often used in cases of cognitive decline, Alzheimer’s disease, and brain health optimization.
Compared to l-carnitine, which is better for fat metabolism, acetyl-l-carnitine excels at enhancing neurotransmitter production, especially acetylcholine, which supports cognitive function.
This is why many experts recommend you take both forms—the classic for the body, and acetyl for the brain.
4. How Does Acetyl-L-Carnitine Support Brain Function?
ALCAR’s ability to cross the blood-brain barrier allows it to directly impact brain function. It’s been studied for its potential to support brain health, slow cognitive decline, and help with neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s disease.
By increasing energy availability in the brain and aiding in neurotransmitter synthesis, acetyl-l-carnitine supplementation helps improve cognitive function, memory, and alertness.
Some studies even suggest acetyl-l-carnitine in dementia cases may improve mental performance and mood, especially in older adults.
5. Can L-Carnitine Help with Fat Loss and Energy Production?
Yes. One of the most discussed benefits of l-carnitine is its ability to promote weight loss and increase energy production. By transporting fatty acids into the mitochondria, l-carnitine helps turn fat into usable energy.
This process not only improves energy metabolism but may also reduce triglyceride levels, enhancing cardiovascular health. It's a key reason many fitness enthusiasts use l-carnitine supplements to boost physical performance and fat-burning.
In essence, l-carnitine plays a role in energy production by ensuring fatty acids are efficiently burned for energy, especially during exercise.
6. Does L-Carnitine Help Manage Type 2 Diabetes?
Emerging research shows that l-carnitine supplementation may positively influence glycemic markers in individuals with type 2 diabetes. It may work by improving insulin function and glucose oxidation, contributing to better insulin sensitivity.
A study that examined the effects of l-carnitine on people with type 2 diabetes found that l-carnitine significantly reduced blood sugar markers and oxidative stress, indicating its therapeutic potential.
Adding l-carnitine as a dietary supplement could support individuals managing diabetes by improving both energy metabolism and glucose control.
7. What Are the Main Benefits of L-Carnitine Supplementation?
The potential benefits of l-carnitine supplementation are diverse:
- Enhances fat metabolism for energy
- Supports brain function
- Reduces oxidative stress
- May aid type 2 diabetes management
- Boosts physical and mental performance
Whether you're aiming for better performance, weight loss, or cognitive function, l-carnitine and alcar could be powerful tools.
Some forms of carnitine esters, like free carnitine, may also play a part in maintaining the body carnitine pool and overall health conditions.
8. How Much L-Carnitine Do You Need Daily?
According to the Office of Dietary Supplements, a standard dose ranges from 500 mg to 2 g of l-carnitine per day, depending on the form and purpose. The optimal amount varies based on health goals, exercise intensity, and dietary intake.
Those with low l-carnitine levels due to vegetarian diets or genetic issues may need higher amounts to restore the body carnitine pool.
It’s essential to discuss your needs with a healthcare provider, especially if you have preexisting health conditions.
9. Who Might Be Deficient in Carnitine?
Carnitine depletion can happen for several reasons:
- Chronic illness affecting the liver and kidney
- Certain medications
- Vegetarian or vegan diets (low red meat and dairy products)
- Genetic disorders affecting the carnitine transporter
If you’re always fatigued, have muscle weakness, or trouble losing fat, you might not have enough l-carnitine. In such cases, carnitine supplementation is worth exploring.
The forms of carnitine vary, but l-carnitine supplements are among the most researched and effective.
10. Should You Take Both L-Carnitine and Acetyl-L-Carnitine?
Absolutely—many experts recommend combining l-carnitine and acetyl-l-carnitine to harness the best of both worlds. This stack supports both physical performance and brain function, aiding in energy metabolism and cognitive benefits simultaneously.
The alc and l-carnitine combo maximizes fatty acid transport, supports the mitochondrion, and enhances alertness and mental clarity.
If you want to improve overall health and disease prevention strategies, combining both forms of this essential nutrient is an efficient approach.
Key Takeaways
- L-carnitine is a naturally occurring amino acid that helps transport fatty acids into the mitochondria for energy production.
- Acetyl-l-carnitine (ALCAR) includes an acetyl group that allows it to cross the blood-brain barrier, supporting brain function and cognitive benefits.
- L-carnitine plays a crucial role in fat metabolism, insulin function, and reducing oxidative stress.
- Studies show l-carnitine supplementation may benefit individuals with type 2 diabetes and those looking to promote weight loss.
- People on vegetarian diets or with carnitine depletion may need to supplement to maintain optimal carnitine levels.
- Combining l-carnitine and acetyl-l-carnitine enhances both physical and mental performance.
- Always consult a health professional before beginning carnitine supplementation.
By understanding how l-carnitine and acetyl-l-carnitine work together, you can take actionable steps toward optimizing your energy metabolism, protecting your brain, and improving overall vitality.












