Acetyl-L-Carnitine: Dosage, Benefits, and Mechanism of Action
Acetyl-L-Carnitine: The Powerful Amino Acid for Energy, Brain Health, and More
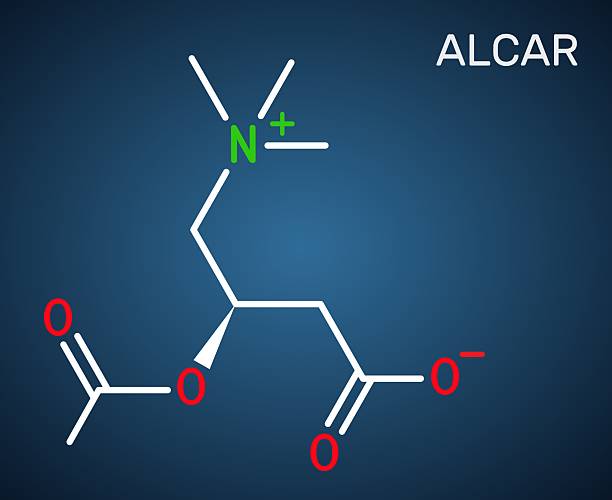
Acetyl-L-carnitine, also known as acetylcarnitine or ALCAR, is a modified form of the amino acid l-carnitine—a naturally occurring compound critical to energy metabolism and brain function.
As both a nutritional supplement and therapeutic agent, acetyl-l-carnitine has captured attention for its potential to treat conditions ranging from type 2 diabetes and male infertility to peripheral neuropathy and cognitive decline.
In this article, we explore the mechanism of action of acetyl-l-carnitine, examine optimal dosage, dive into its use in clinical settings, and explain why it’s become a hot topic in nutritional supplement research.
With insights from systematic reviews, clinical trials, and expert recommendations, this is your complete guide to understanding the benefits and risks of supplementing with acetyl-l-carnitine.
Article Outline
1. What is Acetyl-L-Carnitine and How Is It Different From L-Carnitine?
2. How Does Acetyl-L-Carnitine Work in the Body? Understanding the Mechanism of Action
3. What Are the Benefits of Acetyl-L-Carnitine?
4. Can Acetyl-L-Carnitine Help with Type 2 Diabetes?
5. What Does Research Say? Insights from Clinical Trials and Systematic Reviews
6. How Much Acetyl-L-Carnitine Should You Take? Recommended Dosage and Forms
7. Is It Safe? Side Effects and Precautions to Know
8. Acetyl-L-Carnitine and Brain Health: Memory, Dementia, and Depression
9. Can Acetyl-L-Carnitine Help with Male Infertility and Sperm Motility?
10. Who Should Consider Acetyl-L-Carnitine Supplementation?
1. What is Acetyl-L-Carnitine and How Is It Different From L-Carnitine?
Acetyl-l-carnitine is an amino acid derivative formed by adding an acetyl group to l-carnitine. While both compounds share core functions in fatty acid metabolism, the acetylated version has better bioavailability and crosses the blood-brain barrier more effectively, making it particularly useful for cognitive and neurological health.
Unlike regular carnitine or oral l-carnitine, acetyl-l-carnitine (ALCAR) has specific roles in transporting fatty acids into the mitochondria where they’re used for energy. This transport is critical for cellular energy, especially in high-energy tissues like the brain and muscles.
While carnitine supplementation supports general metabolic health, acetylcarnitine offers additional benefits in mental clarity, memory loss, and peripheral neuropathy management. That’s why many health professionals recommend this form for both physical and neurological support.
2. How Does Acetyl-L-Carnitine Work in the Body? Understanding the Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action behind acetyl-l-carnitine lies in its role as a transporter of long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria. Once inside, these fats are converted into ATP—the body's main energy source—via fatty acid oxidation.
This process not only boosts energy production but also supports oxidative balance. By reducing oxidative damage, acetyl-l-carnitine protects brain cells and nerves from degeneration. It's also involved in regulating lipid metabolism and stabilizing plasma carnitine levels.
Research shows the effect of acetyl-l-carnitine extends to neurotransmitter activity, making it valuable in treating mood disorders and improving cognitive function. Its role in carnitine transport is critical in individuals with carnitine deficiency, allowing better use of stored fats and improving mitochondrial health.
3. What Are the Benefits of Acetyl-L-Carnitine?
One of the most notable benefits of acetyl-l-carnitine is its ability to combat mental decline and age-related cognitive issues. Studies suggest improved memory, attention, and mood in people taking this dietary supplement, especially those with dementia or early-stage Alzheimer's disease.
In addition, acetyl-l-carnitine supports metabolic health by enhancing fatty acid metabolism and reducing fatigue. Athletes and those with chronic fatigue syndrome often report increased stamina and reduced muscle soreness.
Importantly, this compound also contributes to nerve repair. For individuals dealing with diabetic neuropathy or chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, acetyl-l-carnitine offers a natural way to reduce nerve pain and support regeneration.
4. Can Acetyl-L-Carnitine Help with Type 2 Diabetes?
Emerging evidence shows that acetyl-l-carnitine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes may improve insulin sensitivity and reduce nerve complications. According to a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials, ALCAR supplementation helped lower glucose levels and reduce the severity of peripheral neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Carnitine concentrations are often lower in people with diabetes, leading to impaired fat metabolism and mitochondrial dysfunction. Supplementing with acetyl-l-carnitine helps transport fatty acids more efficiently, supporting better glucose utilization and energy output.
Some trials even show improvement in nerve damage and pain associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. As part of a comprehensive care plan, ALCAR may offer a low-risk, high-reward supplement option.
5. What Does Research Say? Insights from Clinical Trials and Systematic Reviews
A growing number of clinical trials and systematic reviews support the efficacy of acetyl-l-carnitine. A Cochrane Database review highlights its benefit in reducing peripheral neuropathy symptoms, particularly in those with diabetes or undergoing chemotherapy.
Another review and meta-analysis of randomized studies found that acetyl-l-carnitine administration significantly improved cognitive function and reduced memory loss in older adults. These effects were consistent even in those with early-stage dementia.
Furthermore, research into the effect of l-carnitine on exercise performance and recovery supports its role in reducing fatigue and enhancing endurance, especially in individuals with carnitine deficiency or low muscle carnitine stores.
6. How Much Acetyl-L-Carnitine Should You Take? Recommended Dosage and Forms
The ideal dosage of acetyl-l-carnitine depends on the condition being treated. For general cognitive support and fatigue, a typical dose is 500–2,000 mg per day. For neuropathy or type 2 diabetes, doses up to 3,000 mg have been used in randomized controlled clinical trials.
Always consult a health care provider before starting any supplement regimen. While acetyl-l-carnitine is available in capsules, powders, and even intravenous forms, most users take it as an oral nutritional supplement.
Note that l-carnitine per day doses should not be confused with acetylated versions. Acetyl-l-carnitine has different pharmacokinetics and benefits, particularly in brain and nerve health.
7. Is It Safe? Side Effects and Precautions to Know
While acetyl-l-carnitine supplementation is generally well tolerated, some users report mild side effects such as nausea, restlessness, or headache. Serious adverse effects are rare but can include interactions with medications like valproic acid.
People with preexisting medical conditions should exercise caution and consult their doctor. Studies report fewer adverse effects compared to other cognitive enhancers or metabolic drugs.
In clinical use, acetyl-l-carnitine in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy and other conditions showed promising results with minimal risk, but individual responses can vary.
8. Acetyl-L-Carnitine and Brain Health: Memory, Dementia, and Depression
One of the most exciting applications of ALCAR is in brain health. Research shows improvements in memory loss, mental fatigue, and even symptoms of depression. In some cases, acetyl-l-carnitine was found to be as effective as conventional antidepressants with fewer side effects.
The effect of acetyl-l-carnitine on age-related mental decline and Alzheimer's disease has been well-documented in systematic reviews. This makes it a valuable tool in maintaining cognitive function as we age.
Furthermore, ALCAR may increase the effect of l-carnitine when taken together, improving neurotransmitter activity and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain.
9. Can Acetyl-L-Carnitine Help with Male Infertility and Sperm Motility?
Several studies indicate that acetyl-l-carnitine for the treatment of male infertility may improve sperm motility, count, and overall function. Since carnitine plays a critical role in energy production in sperm cells, higher levels can directly impact reproductive health.
In trials involving men with fertility challenges, supplementation with both l-carnitine and acetyl-l-carnitine showed significant improvement in sperm quality and pregnancy rates. This benefit is likely due to enhanced lipid metabolism and reduced oxidative stress in sperm cells.
This makes ALCAR a valuable dietary supplement option for men dealing with age-related or stress-related fertility issues.
10. Who Should Consider Acetyl-L-Carnitine Supplementation?
Those dealing with chronic fatigue, type 2 diabetes, peripheral neuropathy, or cognitive decline could benefit from acetyl-l-carnitine therapy. Similarly, older adults, athletes, and individuals with carnitine deficiency may see improved energy, recovery, and mental clarity.
Children with neurological disorders like fragile x syndrome and individuals with liver conditions such as patients with chronic hepatitis have also been studied, showing varying levels of success.
Before deciding to take acetyl-l-carnitine, speak with your doctor to assess safety, especially if you're on medications or have underlying health issues.
Key Takeaways
- Acetyl-l-carnitine is a powerful amino acid derivative that supports energy, brain, and nerve health.
- It improves fatty acid transport into mitochondria, increasing ATP production and reducing oxidative damage.
- Effective for treating type 2 diabetes, peripheral neuropathy, male infertility, and cognitive decline.
- Doses typically range from 500 to 3,000 mg per day, depending on the condition and individual needs.
- Supported by systematic reviews, clinical trials, and the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.
- Side effects are generally mild, though consulting a health care provider is essential.
- ALCAR crosses the blood-brain barrier more effectively than standard l-carnitine, making it superior for cognitive use.
- Useful in improving sperm motility, reducing memory loss, and mitigating symptoms of depression.
- Notable for having fewer adverse effects compared to many pharmaceutical alternatives.
- Ideal for individuals with carnitine deficiency, aging-related issues, or increased energy demands.